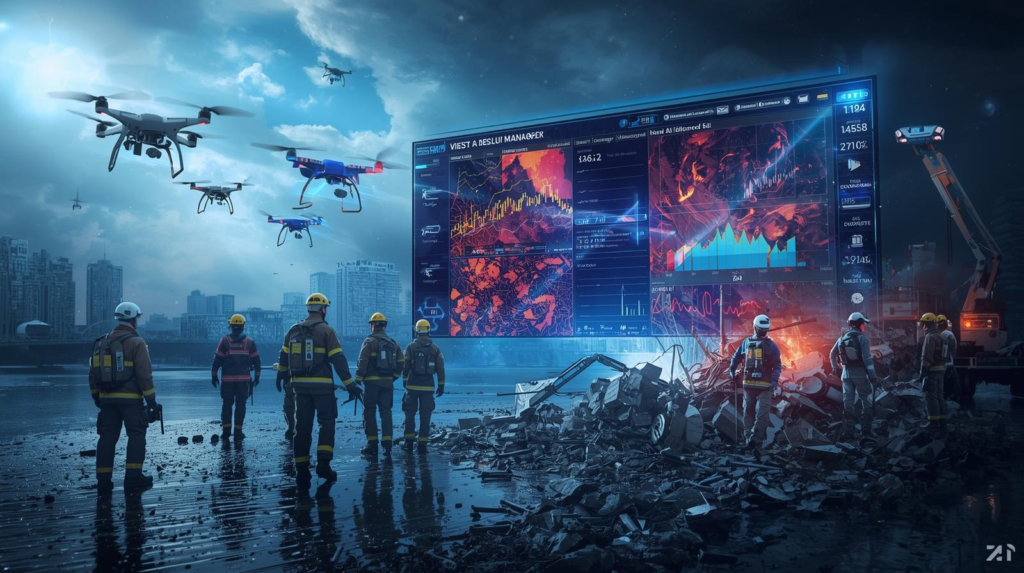
When natural disasters strike, the difference between chaos and order, survival and loss, often lies in the speed and accuracy of response. Traditionally, disaster management has relied on human expertise, manual prediction models, and large-scale mobilization of emergency forces. But in an age where climate change is intensifying cyclones, floods, wildfires, and earthquakes, traditional methods alone are no longer sufficient. Increasingly, artificial intelligence is stepping in as the invisible but crucial partner that enhances prediction, coordination, and relief efforts. This is where the significance of the AI in disaster management case study comes into sharp focus, demonstrating how algorithms and predictive systems can function as unseen first responders. At AixCircle, we believe that the story of AI in resilience is not just about technology but about saving human lives and preparing societies for future crises.
The Cyclone Amphan Case Study: A Turning Point for AI Disaster Response
In May 2020, Cyclone Amphan swept across India and Bangladesh, becoming one of the most devastating cyclones in decades. With winds exceeding 240 km/h, the storm left behind a trail of destruction, displacing millions and damaging infrastructure worth billions of dollars. The challenge was monumental: predicting the cyclone’s path accurately, ensuring timely evacuations, and coordinating relief supplies in the middle of a pandemic.
This is where AI disaster response played a critical role. Using advanced satellite data combined with deep learning algorithms, AI models issued 72-hour early warnings that significantly improved upon traditional meteorological forecasts. The accuracy of these predictions allowed governments to prepare evacuation strategies that moved millions of people out of high-risk zones. This single intervention alone illustrates the life-saving power of AI in disaster management case study contexts.
But the role of AI didn’t end there. Predictive flood mapping systems used historical rainfall data, soil absorption rates, and geographical contours to identify which villages were most vulnerable to flooding after the cyclone. Local authorities, guided by AI recommendations, could prioritize evacuations and resource allocation. Additionally, AI-powered chatbots disseminated verified safety instructions in regional languages, reaching communities where literacy or misinformation could have otherwise put lives at risk. The outcomes were remarkable: tens of thousands of lives were saved, and despite the scale of Amphan’s destruction, casualty numbers were significantly lower than similar disasters in previous decades.
AI as the Invisible First Responder
The Cyclone Amphan case underscores a larger truth: artificial intelligence is becoming the AI first responder in modern crisis situations. Unlike human teams that need to physically reach disaster zones, AI systems analyze massive datasets in real time, issuing insights and alerts before damage spirals out of control. This proactive approach is at the heart of every AI in disaster management case study, proving that speed and foresight can mean the difference between life and death.
For example, during Amphan, while meteorological departments were still processing raw data, AI systems had already run thousands of simulations predicting not just the cyclone’s landfall point but also secondary impacts like flooding, crop damage, and disease risks. This ability to “see the future” through predictive AI models transforms disaster preparedness into a science-driven effort rather than a reactionary scramble. At AixCircle, we see this shift as one of the most powerful outcomes of applying AI for natural disasters.
The Role of Predictive AI Models in Disaster Preparedness
Predictive models are at the heart of AI disaster response strategies. These systems draw from satellite imagery, IoT sensors, weather forecasts, and historical records to simulate scenarios with astonishing precision. In the AI in disaster management case study of Cyclone Amphan, predictive flood mapping helped authorities identify “red zones” where damage would be most severe. This precision allowed emergency teams to deploy relief supplies and medical units strategically, rather than dispersing resources randomly.
Predictive AI models go beyond weather-related disasters. For instance, earthquake-prone regions in Japan and California are experimenting with AI that can detect micro-seismic patterns and issue early warnings seconds before tremors reach urban centers. While a few seconds may sound negligible, they can be enough to halt trains, shut down power grids, and save thousands of lives. Similarly, wildfire-prone regions in Australia are deploying AI that scans satellite imagery to detect “hot spots” invisible to the human eye, issuing evacuation orders before flames become uncontrollable.
Each AI in disaster management case study emphasizes one lesson: the more data AI has access to, the more lives it can help save. By training algorithms on diverse datasets, AI systems are becoming increasingly adept at anticipating crises before they escalate into catastrophes.
AI for Natural Disasters: A Humanitarian Lens
Technology, however, is only meaningful when applied for human good. When we discuss AI for natural disasters, it’s important to focus on the human side of the equation — the lives protected, the communities preserved, and the hope restored in moments of despair. In the Cyclone Amphan case, beyond flood mapping and early warnings, AI-powered communication platforms played a crucial role in combating misinformation.
During disasters, rumors and false news can spread faster than official updates, leading to panic or dangerous decisions. AI-driven natural language processing systems were deployed to filter and disseminate only verified updates, ensuring that vulnerable communities received accurate guidance. This communication aspect of AI disaster response is often overlooked but remains vital. For many, the chatbot alerts sent in Bengali or Odia were the only reliable source of information in the chaos.
At AixCircle, we view AI in disaster management case study frameworks as more than technological experiments — they are humanitarian stories, where innovation meets empathy.
Beyond Amphan: Global Applications of AI Disaster Response
While Cyclone Amphan serves as a powerful AI in disaster management case study, similar applications are unfolding worldwide. In the United States, AI models are used to predict hurricane intensities and track wildfires in California. In China, drones powered by AI map earthquake damage within hours, allowing rescue teams to prioritize areas where survival chances are highest. In Africa, AI is being deployed to predict droughts, enabling governments to stockpile food and water resources before crises escalate into famine.
This global perspective strengthens the argument that AI disaster response is not confined to one region or disaster type. From tsunamis to epidemics, the adaptability of AI systems makes them versatile tools in the arsenal of modern disaster preparedness. Moreover, the scalability of AI solutions means that even resource-constrained nations can benefit from relatively low-cost systems like AI-powered chatbots, predictive mapping, and automated supply chain logistics.
Future Potential: Expanding the Role of AI First Responders
Looking ahead, the potential applications of AI in disaster management are vast. Imagine fleets of AI-powered drones flying into post-disaster zones to map destruction in real time, transmitting data that allows relief teams to act faster. Consider predictive healthcare systems that can forecast outbreaks of diseases like cholera or malaria after floods, enabling preemptive vaccination campaigns. Think about AI-driven supply chains that autonomously route food, water, and medicine to disaster-hit regions, minimizing delays caused by human error or bureaucratic bottlenecks.
These innovations, when combined, position AI as not just a tool but as an AI first responder — an unseen but indispensable ally in moments of crisis. Each future AI in disaster management case study will likely demonstrate an even deeper integration of algorithms into every stage of the disaster lifecycle: prediction, prevention, response, and recovery. At AixCircle, we believe the future of resilience lies in embracing these possibilities with both urgency and responsibility.
The Challenges: Ethics, Privacy, and Trust
Of course, no discussion of the AI in disaster management case study format would be complete without acknowledging challenges. Data privacy remains a major concern, as disaster response often requires collecting sensitive information about individuals and communities. Who controls this data, and how it is safeguarded, will shape public trust in AI disaster response systems.
Another challenge is bias in predictive AI models. If algorithms are trained on incomplete or skewed datasets, they may misidentify at-risk areas or neglect vulnerable populations. In disaster scenarios, such mistakes can cost lives. Therefore, transparency and accountability are as important as technological capability. At AixCircle, we emphasize that the promise of AI for natural disasters can only be fully realized when ethical considerations are embedded into system design.
Conclusion
Cyclone Amphan may have been one of the first major demonstrations of AI’s life-saving potential, but it will not be the last. Every new AI in disaster management case study reinforces the reality that AI is no longer a futuristic luxury — it is a necessity in a world where natural disasters are intensifying due to climate change. By serving as an unseen AI first responder, AI not only augments human capacity but also redefines what resilience looks like in the 21st century.
The AI disaster response story is still being written, and as more countries adopt predictive AI models, the gap between vulnerable and prepared communities will widen unless these tools are equitably deployed. At AixCircle, our commitment is to ensure that discussions around AI for natural disasters remain centered on humanity: saving lives, protecting livelihoods, and building stronger, more resilient societies.
The future of disaster preparedness will not be about whether humans or AI lead the response, but about how they work together. In this collaboration lies the hope that when the next storm, flood, or earthquake strikes, AI will already be there — quietly, invisibly, and decisively — as the unseen first responder.